understanding and addressing depression
Now that spring is well on its way, is your mood picking up? If you’re still feeling the “blahs” – low energy, persistent sadness, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and a loss of interest in activities you once enjoyed – this might be more than the winter blues.
While Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a well-known culprit for winter blues, it’s crucial not to overlook other underlying issues that may contribute to depressive symptoms. Booking an appointment with your ND can provide valuable insights into your mental and physical well-being. During your visit, we can explore various factors contributing to depression, including hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, lifestyle habits, and environmental stressors.
By taking a comprehensive approach, we can tailor a treatment plan to address your unique needs. This may include a combination of dietary adjustments, supplementation, herbal remedies, lifestyle modifications, and acupuncture. Additionally, we will work collaboratively with you to uncover any potential root causes and develop strategies for long-term wellness.
Here a few tips to consider as we hop into spring…
Protein
Foods that are rich in protein contain amino acids that help produce neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin. If your protein intake is low, you may experience low mood. Most adults require 1g of protein per kilogram of body weight. Fortunately, it is easy to increase your protein intake – here are some easy ideas to snack on:
A handful of unsalted almonds, walnuts, and/or pecans
A hard-boiled egg
An apple with 2 tbsp nut butter of your choice
Sausage sticks or jerky (aim for ones with no fillers)
Edamame
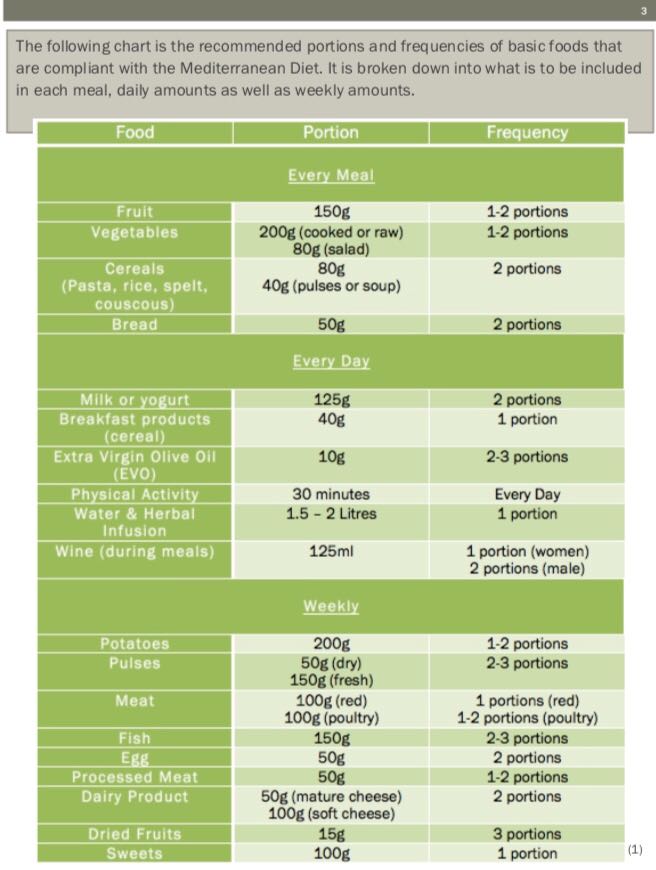
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is a diet high in fish, legumes, whole grains, vegetables, fruits, seeds, and olive oil. It is low in high fat meats and dairy products. Following the Mediterranean Diet has been shown to be protective against depression at all ages throughout a person’s lifespan. For more information, check out our past blog post.
Exercise
Adults (including seniors) should get at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week[i]. Think that’s a stretch? Here are some ways to incorporate more movement into your day:
Do squats or lunges while you brush your teeth
Park farther away from stores or work
Take the stairs
Spontaneous dancing (at home OR in public 😊)
Deep clean something
Get up and move your body during commercial breaks – marching in place, jumping jacks, walking lunges across the room…be creative!
Sunshine
Exposure to sunlight increases serotonin levels in the brain. While you may be taking a Vitamin D supplement to keep your levels up, being in the sunshine is the best source of natural Vitamin D[ii]. In order to optimize your exposure, we recommend spending anywhere between 5-30 minutes each day outside[iii] – and while you’re out there, why don’t you get in that little extra bit of exercise and take a walk around the block?
Did you know that Vitamin D is not typically tested when you have bloodwork completed by your physician? Many people may be deficient in this important vitamin and not even know it. If this is something you are concerned about or would like to know more, bring it up with your naturopathic doctor - it may be worth investigating!
Don’t forget…
You don’t have to navigate depression alone. Your mental health matters every day and every season of the year.
[i] https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/physical-activity-tips-adults-18-64-years.html
[ii] Raymond-Lezman JR, Riskin SI. Benefits and Risks of Sun Exposure to Maintain Adequate Vitamin D Levels. Cureus. 2023 May 5;15(5):e38578. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38578. PMID: 37284402; PMCID: PMC10239563.
[iii] Srivastava SB. Vitamin D: Do We Need More Than Sunshine? Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021 Apr 3;15(4):397-401. doi: 10.1177/15598276211005689. PMID: 34366736; PMCID: PMC8299926.